Our adrenal glands are tiny glands located on top of each kidney. They play a crucial role in producing hormones that help control blood pressure, metabolism, and stress responses. When we talk about adrenal cancer, we refer to a serious condition where cancer cells form in the tissue of the adrenal glands. Early recognition and proper treatment of this condition are important to ensure the best outcomes.
Understanding Adrenal Cancer and Tumor Types
Adrenal cancer occurs when cells in the adrenal glands grow uncontrollably. There are two main types: benign tumors, which are non-cancerous, and malignant tumors, which are cancerous. Malignant tumors can grow quickly and spread to other body parts, making early detection crucial.
Statistics show that adrenal cancer is rare, affecting approximately 1 to 2 persons per million worldwide each year. While it’s not common, the occurrence of benign tumors in the adrenal glands is more frequent.
Some common misconceptions include believing that all tumors on the adrenals are cancerous or that everyone gets the same symptoms. However, understanding the differences between benign and malignant tumors is key to knowing when and how to seek help.
Recognizing Common and Hormone-Specific Symptoms
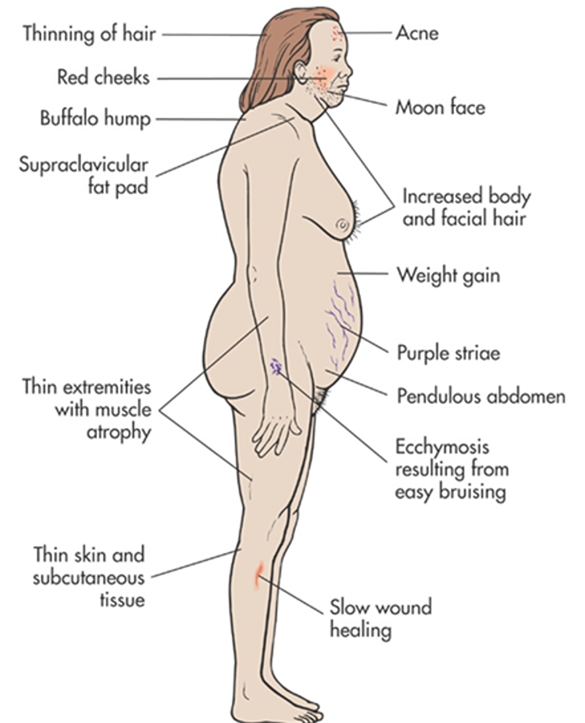
If a tumor in the adrenal gland produces hormones, it can cause various symptoms. These may include:
- Weight gain and muscle weakness.
- High blood pressure that is hard to control.
- In women, increased body hair or irregular menstruation.
- In children, signs of early puberty.
Symptoms vary depending on whether the tumor affects hormones like androgens or estrogens. Recognizing these signs is important for early diagnosis of adrenal cancer or related conditions.
Identifying Behavioral and Physical Changes
Aside from hormone-related symptoms, adrenal cancer may cause physical signs such as pain in the abdomen or loss of appetite. People may also experience changes in mood or emotions due to stress about their health.
It’s essential to stay vigilant about any changes you notice in your body and seek medical advice promptly. Early action and monitoring can significantly influence treatment outcomes.
Risk Factors, Causes, and Seeking Medical Attention
Genetic factors may increase the risk of adrenal cancer. If someone in your family has had adrenal or other types of cancer, your risk could be higher. Certain conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome, can also elevate your risk.
Adrenal cancer can affect anyone, but age and gender may play a role. This cancer is more common in children under 5 and adults between 40 and 50.
If you experience any signs, consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment options give the best chance for effective management.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing adrenal cancer involves a series of medical consultations, screenings, and tests like blood tests or imaging. These helps pinpoint the presence and extent of the tumor.
Treatment often involves surgery to remove the affected adrenal gland, which is known as adrenalectomy. Radiation and medications are other options to manage and treat cancer. New treatment modalities are continually being developed, especially in major cities in India, offering more hope to patients.
Understanding these methods helps take away the complexity and fear associated with the adrenal cancer treatment process.
Living Beyond Adrenal Cancer
Getting diagnosed with adrenal cancer can be a life-changing experience. Tackling emotional and psychological impacts is crucial for both patients and families. Support groups and psychological avenues can provide the much-needed emotional support.
Maintaining a good quality of life involves taking control of your health. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management strategies can help you live a fulfilled life after treatment.
Empowering oneself with knowledge and support enhances well-being, making it easier to navigate life beyond an adrenal cancer diagnosis. Remaining hopeful and informed are key components of long-term recovery and maintaining quality of life.